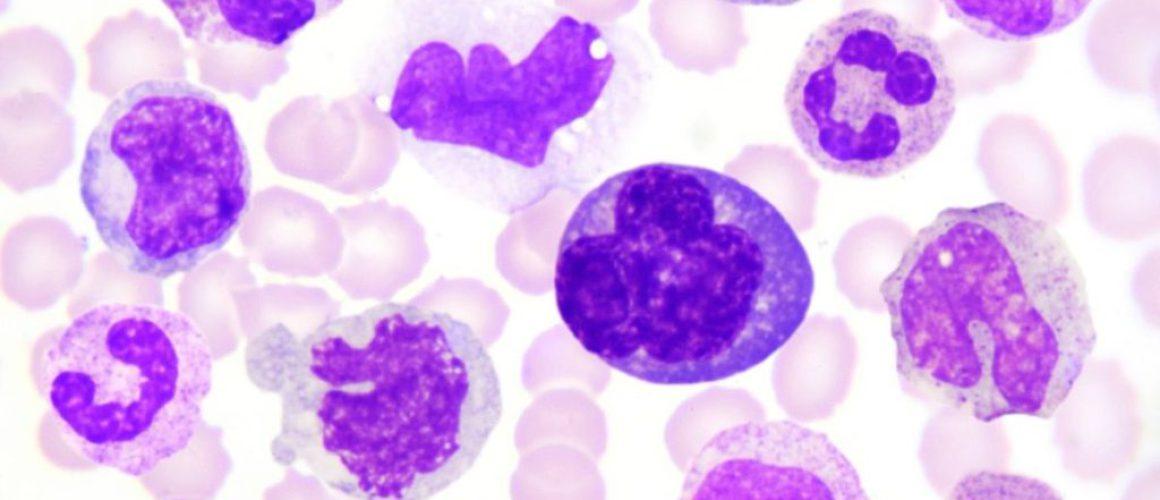
White blood cell types and functions
Table of Contents
Key Summary Table: White Blood Cell Types
| White Blood Cell Type | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Neutrophils | First to arrive at the site of an infection, neutralizing pathogens through phagocytosis. |
| Lymphocytes | Comprised of T cells (directly kill infected cells) and B cells (produce antibodies to neutralize pathogens). |
| Monocytes | Transform into macrophages to engulf and destroy pathogens and cellular debris. |
| Eosinophils | Primarily deal with parasitic infections and play a role in allergic reactions. |
| Basophils | Release histamine during allergic reactions and asthma attacks, contributing to the body’s inflammatory response. |
Diving into the world of hematology, we encounter a fascinating cast of characters: our white blood cells. Each type, from neutrophils to lymphocytes, plays a unique role in our health. Stick around to unravel the mystery of these cellular superheroes and their functions.
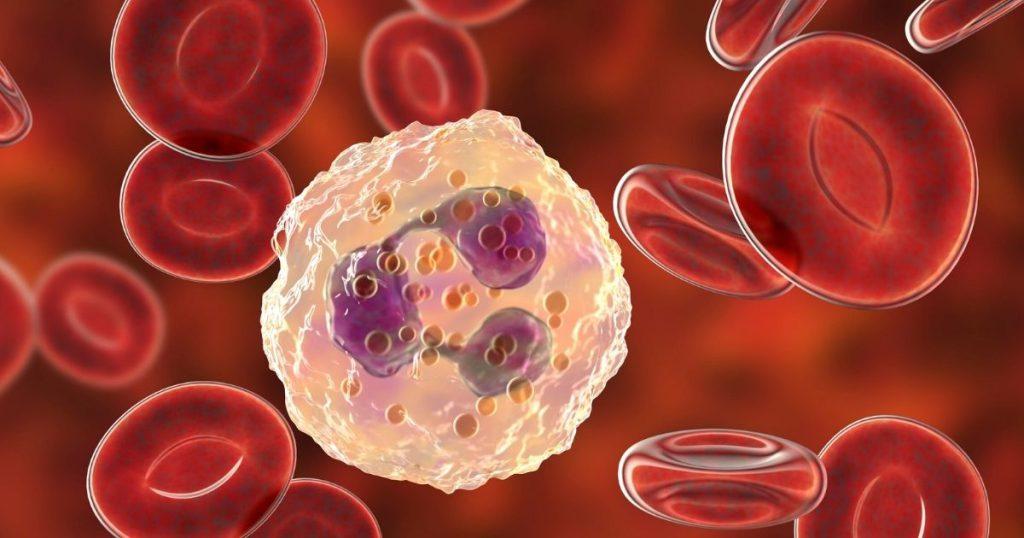
Introduction
As a student of medical technology, I’ve always been fascinated by the intricate world of hematology, particularly the diverse types and functions of white blood cells. These microscopic warriors are the backbone of our immune system, defending our bodies against harmful invaders and playing a crucial role in maintaining our overall health. In this article, we will delve into the world of white blood cells, exploring their types, functions, and the vital role they play in our immune response.
Understanding the types and functions of white blood cells is fundamental to our understanding of the human immune system. These tiny cells play a crucial role in defending our bodies against harmful invaders
Understanding Hematology
Before we dive into the specifics of white blood cells, let’s take a moment to understand the broader field of hematology. Hematology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the study of blood, blood-forming organs, and blood diseases. It encompasses a wide range of topics, from blood cell production to blood clotting mechanisms. But one of the most fascinating aspects of hematology is the study of white blood cells. These cells, also known as leukocytes, are a key component of our immune system and play a vital role in defending our bodies against infections and diseases.
Key Terms in Hematology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Hematology | The branch of medicine that focuses on the study of blood, blood-forming organs, and blood diseases. |
| Leukocytes | Another term for white blood cells. |
| Pathogen | A bacterium, virus, or other microorganism that can cause disease. |
The Importance of White Blood Cells
White blood cells, or leukocytes, are the unsung heroes of our immune system, working tirelessly to protect us from harmful invaders. They are like the body’s internal police force, constantly patrolling our bloodstream for signs of trouble. When they encounter a pathogen, such as a bacteria or virus, they spring into action, neutralizing the threat and helping to keep us healthy. But white blood cells aren’t just a single type of cell – they come in several different forms, each with its own unique role in our immune response.
Key Aspects of Hematology
- Study of blood and blood-forming organs.
- Investigation of blood diseases and disorders.
- Examination of blood cells and their functions.
Different Types of White Blood Cells
While they may all share a common goal, not all white blood cells are created equal – each type has a unique role in our immune response. There are five main types of white blood cells: neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Neutrophils are the most common type of white blood cell and are the first to arrive at the scene of an infection. Lymphocytes, which include T cells and B cells, are responsible for the body’s adaptive immune response, allowing us to build immunity to specific pathogens. Monocytes, on the other hand, are the largest type of white blood cell and can transform into macrophages to engulf and destroy pathogens.
Characteristics of White Blood Cell Types
| White Blood Cell Type | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Neutrophils | Most common type of white blood cell. |
| Lymphocytes | Includes T cells and B cells. |
| Monocytes | Largest type of white blood cell. |
| Eosinophils | Involved in combating parasitic infections. |
| Basophils | Least common type of white blood cell. |
Functions of White Blood Cell Types
Now that we’ve identified the different types of white blood cells, let’s delve into the specific functions of each type. Neutrophils, as mentioned earlier, are the body’s first line of defense against infection. They are highly mobile and can quickly reach the site of an infection to begin neutralizing pathogens. Lymphocytes, on the other hand, provide a more targeted response. T cells can directly kill infected cells, while B cells produce antibodies that can neutralize pathogens. Monocytes, which can transform into macrophages, are like the body’s garbage collectors, engulfing and destroying pathogens and cellular debris.
Unique Features of Each White Blood Cell Type
- Neutrophils: Highly mobile and quick to respond to infections.
- Lymphocytes: Provide a targeted immune response.
- Monocytes: Can transform into macrophages.
- Eosinophils: Play a key role in allergic reactions.
- Basophils: Release histamine during allergic reactions.
The Role of White Blood Cells in Disease
Beyond their normal functions, white blood cells can also provide us with crucial insights into various diseases. For example, an unusually high or low white blood cell count can be an indicator of an underlying health issue, such as an infection, autoimmune disease, or even cancer. By studying white blood cells, researchers can gain valuable insights into these diseases, potentially leading to new treatments and therapies.
The immune system is not a single entity. Instead, it’s a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs, with white blood cells serving as the frontline soldiers in the body’s defense against pathogens.

Conclusion
Understanding the types and functions of white blood cells is not just fascinating, it’s fundamental to our understanding of the human immune system. These tiny cells play a crucial role in defending our bodies against harmful invaders, and their importance cannot be overstated. As we continue to explore the complex world of hematology, we can look forward to new discoveries and insights that will deepen our understanding of these vital cells.
If you find the captivating world of hematology as intriguing as I do, continue exploring this fascinating field. Visit my Hematology index page or the Hematology category for more in-depth articles and insights.
Other posts of interest: Blood components and their functions and Blood Types and Compatibility
Disclaimer
This article is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. The information contained herein is not a substitute for and should never be relied upon for professional medical advice. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are white blood cells?
White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are cells of the immune system that defend the body against both infectious diseases and foreign invaders. They are a key component of our immune system and play a vital role in maintaining our overall health.
How many types of white blood cells are there?
There are five main types of white blood cells: neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Each type has a unique role in our immune response.
What is the function of neutrophils?
Neutrophils are the most common type of white blood cell and are the first to arrive at the scene of an infection. They neutralize pathogens through a process known as phagocytosis, where they engulf and destroy the invading microorganisms.
What are lymphocytes and what do they do?
Lymphocytes include T cells and B cells. T cells can directly kill infected cells, while B cells produce antibodies that can neutralize pathogens. They are responsible for the body’s adaptive immune response, allowing us to build immunity to specific pathogens.
What role do monocytes play in the immune system?
Monocytes are the largest type of white blood cell and can transform into macrophages to engulf and destroy pathogens and cellular debris. They are like the body’s garbage collectors, cleaning up after an immune response.
What is hematology?
Hematology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the study of blood, blood-forming organs, and blood diseases. It encompasses a wide range of topics, from blood cell production to blood clotting mechanisms.
How do white blood cells help us understand diseases?
An unusually high or low white blood cell count can be an indicator of an underlying health issue, such as an infection, autoimmune disease, or even cancer. By studying white blood cells, researchers can gain valuable insights into these diseases, potentially leading to new treatments and therapies.
Further reading
What Are White Blood Cells? – Health Encyclopedia – URMC
Sean Schepers is a third-year Medical Technology student at Mahidol University with a passion for all things health and medicine. His journey into the world of medicine has led him to explore various fields. Sean's blog posts offer a unique perspective, combining his academic insights with personal experiences. When he's not studying or blogging, Sean enjoys keeping up with politics and planning his future career in medicine.
In addition to his studies, Sean serves as the chairman of the Rights, Liberties, and Welfare Committee, a role that reflects his commitment to advocacy and social justice. Beyond his academic pursuits, Sean offers tutoring services in English and Biology, further demonstrating his dedication to education and mentorship. His journey is one of continuous discovery, and he invites others to join him as he explores the dynamic and transformative world of medical technology.