What Does a Molecular Biologist Do?
Table of Contents
Introduction
Hello there! If you’ve ever wondered what a molecular biologist does, you’ve come to the right place. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of molecular biology, exploring the daily tasks of a molecular biologist, the tools they use, and the impact they have on our lives.
What is Molecular Biology?
Molecular biology, in its essence, is a fascinating realm of science that delves deep into the life-sustaining activities of living organisms. It’s like the backstage pass to the grand concert of life, revealing the intricate details of the performers – the molecules. These molecules, each playing their part in the symphony of biological processes, are the stars of this field.
The spotlight in molecular biology shines on the structures and functions of these molecules. We’re talking about the big players here – DNA, RNA, proteins, and even the smaller yet significant ones like nucleotides and amino acids. Each molecule, with its unique structure, has a specific role, and understanding this is like deciphering the script of a play. It’s about knowing who does what, when, where, and how.
But molecular biology isn’t just a static field where we merely observe these molecules. Oh no, it’s a dynamic and rapidly evolving discipline. It’s like a detective’s work, where we’re constantly unravelling new mysteries and pushing the boundaries of our understanding. The advancements in technology and techniques are the magnifying glasses that bring us closer to the truth.
From the invention of the microscope to the development of DNA sequencing, each advancement peels back another layer of the molecular world. And with each layer, we gain a deeper understanding of the biological activities that keep the wheels of life turning.
So, to put it simply, molecular biology is more than just a field of science. It’s a journey into the heart of life itself, a journey that’s as complex as it is captivating. And as a molecular biologist, I’m just a traveler, eager to explore and share the wonders that this journey unveils.
The Daily Tasks of a Molecular Biologist
As a third-year medical technology student, I can tell you that the life of a molecular biologist is far from monotonous. It’s a whirlwind of activities that revolve around the microscopic world of molecules and cells. Let me walk you through a typical day in the life of a molecular biologist, at least as I envision it from my current studies and experiences.
The day usually kicks off in the lab, the molecular biologist’s playground. Here, they immerse themselves in a world of experiments designed to unravel the intricate dance of life’s building blocks. They might be sequencing DNA, a process that reads the unique genetic code of an organism. Or perhaps they’re purifying proteins, isolating these complex molecules to study their structure and function. They could also be analyzing gene expression, investigating how different environmental conditions can turn genes “on” or “off.”
As the day progresses, the molecular biologist trades their lab coat for a computer. The afternoon is often dedicated to data analysis, a critical part of any scientific research. The results of their morning experiments need to be interpreted, conclusions drawn, and hypotheses refined. This isn’t just about looking at numbers and graphs; it’s about telling a story of how biological processes work at the molecular level.
This is where bioinformatic tools come into play. In the world of molecular biology, data is abundant. From genome sequences to protein structures, the amount of information can be overwhelming. Bioinformatic tools are like a compass in this sea of data, helping molecular biologists navigate, manage, and make sense of the information they’ve gathered.
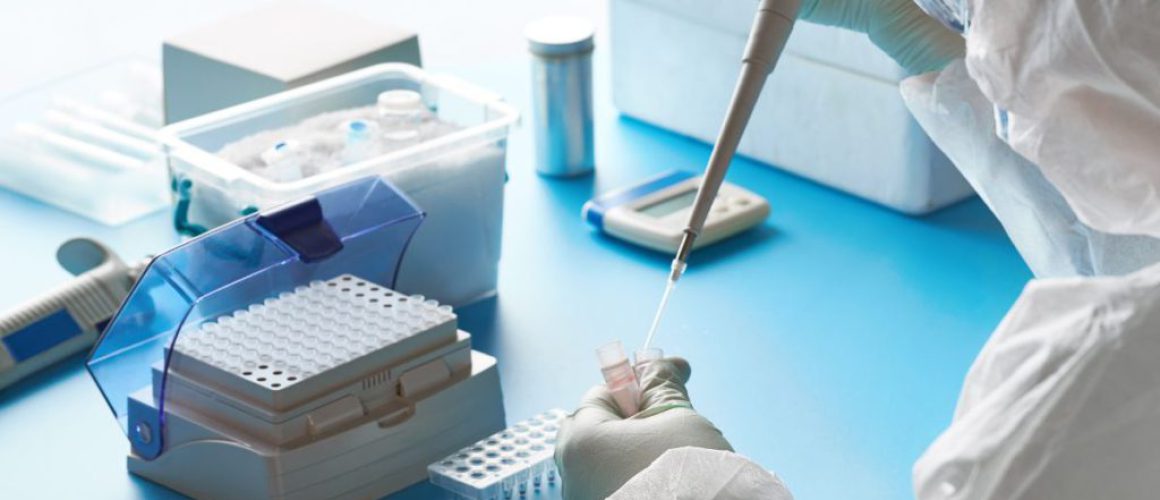
The Tools of the Trade
As a third-year medical technology student, I’ve had the privilege of getting up close and personal with some of the tools that molecular biologists use in their work. It’s a fascinating mix of traditional lab equipment and cutting-edge technology that allows us to delve into the very building blocks of life.
Let’s start with the basics. Any molecular biology lab will be equipped with microscopes and centrifuges. Microscopes, as you probably know, allow us to see tiny structures that are invisible to the naked eye. They’re essential for examining cells and other small samples. Centrifuges, on the other hand, are used to separate different components of a sample based on their densities. This can be crucial for isolating specific cells, proteins, or other molecules for further study.
But the tools of a molecular biologist go far beyond these basics. For instance, electron microscopes take microscopy to a whole new level. They use a beam of electrons instead of light to magnify the sample, allowing us to see structures that are even smaller than those visible with a light microscope. This can be incredibly useful for studying the intricate details of cells and molecules.
Then there’s the DNA sequencer. This remarkable piece of technology can read the sequence of nucleotides in a DNA molecule. This information is crucial for understanding how genes function and how they contribute to different traits and diseases. As a student, I’ve been awed by the power of this tool to unlock the secrets of our genetic code.
But the tools of a molecular biologist aren’t just physical. They also include a variety of software tools for data analysis and visualization. These tools allow us to make sense of the vast amounts of data that molecular biology experiments can generate. They can help us identify patterns, make comparisons, and draw conclusions from our data. And with the rise of bioinformatics, these tools are becoming increasingly important in molecular biology.
The Impact of Molecular Biology
I’ve come to appreciate the far-reaching impact of molecular biology. It’s a field that doesn’t just exist in the confines of a lab or the pages of a textbook. Instead, it spills over into various aspects of our lives, influencing everything from environmental science to pharmaceuticals and academic research.
Let’s start with environmental science. This is a field that’s all about understanding our natural world and how we interact with it. And molecular biology plays a crucial role here. For instance, molecular biology techniques are often used to study the effects of pollution on wildlife. By examining the DNA of animals exposed to pollutants, scientists can gain insights into the genetic changes that these pollutants cause. This can help us understand the long-term effects of pollution on wildlife populations and ecosystems. As someone who cares deeply about our environment, I find this application of molecular biology both fascinating and incredibly important.
Then there’s the pharmaceutical industry. Here, the work of molecular biologists is directly tied to the development of new drugs and therapies. By studying the molecular mechanisms of diseases, molecular biologists can identify potential targets for new drugs. They can also contribute to the design and testing of these drugs, ensuring that they are effective and safe. This aspect of molecular biology is particularly close to my heart, as it’s where science meets healthcare, leading to real-world solutions that can improve people’s lives.
And of course, we can’t forget about academia. In universities and research institutions around the world, molecular biologists are pushing the boundaries of our knowledge about life at the molecular level. Their research can lead to new theories, new techniques, and new understandings of how life works. As a student, I’m constantly amazed by the discoveries coming out of these academic labs. They inspire me to keep learning, keep questioning, and keep exploring the fascinating world of molecular biology.
Compliance and Safety
Like all scientists, molecular biologists must adhere to strict safety procedures in their work. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, following protocols for handling biological samples, and ensuring that their work complies with ethical guidelines.
Conclusion
Being a molecular biologist is about more than just conducting experiments. It’s about curiosity, creativity, and a deep desire to understand the mysteries of life at the molecular level. Whether they’re in the lab, at the computer, or presenting their findings to others, molecular biologists play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the world around us.
This post is part of my Molecular Biology category. Also check out my series on Molecular Biology.
Other posts of interest: An Introduction to Molecular Biology: Unraveling the Basics and Gene editing tools (e.g., CRISPR/Cas9)
This post is part of the Career Prospects Category. For more check out Medical Technology Career Prospects: A Student’s Perspective
Other posts in career prospects: Clinical laboratory technologist/medical technologist and Histotechnologist
Disclaimer: This blog post is intended for informational purposes only. While every attempt has been made to ensure the accuracy of the information provided, it is not intended as professional or scientific advice. Always consult with a professional in the field for accurate information.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a molecular biologist do?
A molecular biologist studies the composition, structure, and interactions of cellular molecules such as nucleic acids and proteins that carry out the biological processes essential for the cells’ functions and maintenance. They perform complex research projects, such as sequencing genomes, studying molecular pathways, and researching how genes are transferred from generation to generation.
What are examples of molecular biology?
Examples of molecular biology include DNA sequencing, gene cloning, PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), gel electrophoresis, and studying the interactions between different cell systems, such as protein synthesis via the interaction of DNA and RNA.
Is molecular biology the same as microbiology?
Molecular biology and microbiology are not the same. While both are branches of biology, molecular biology focuses on the molecular mechanisms of life, including how DNA, RNA, and proteins interact. On the other hand, microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, archaea, fungi, and protozoa.
What is the basic concept of molecular biology?
The basic concept of molecular biology is to understand the interactions between the various systems of a cell, including the interrelationship of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis and how these interactions are regulated.
Why do people study molecular biology?
People study molecular biology to understand the molecular mechanisms of the processes of life. It can lead to important discoveries such as new drug targets for diseases, understanding genetic diseases, and developing genetically modified organisms in agriculture.
What are the 4 types of biological molecules?
The four types of biological molecules, often referred to as the molecules of life, are nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Is molecular biology hard?
Molecular biology can be challenging as it involves understanding complex concepts and processes at the molecular level. It also requires a strong background in other areas of science, including chemistry, genetics, and biochemistry.
Is molecular biology a good career?
Molecular biology can be a rewarding career. It offers the opportunity to contribute to important scientific discoveries and advancements. Careers in molecular biology can range from research and academia to roles in healthcare, agriculture, and biotechnology industries.
What can I do if I study molecular biology?
Studying molecular biology can lead to various career paths. You could work as a research scientist, laboratory technician, or academic lecturer. You could also work in the pharmaceutical industry, developing new drugs, or in the agricultural industry, improving crop varieties.
Do doctors know molecular biology?
Doctors have a basic understanding of molecular biology. It’s a crucial part of medical education as it provides the foundation for understanding the molecular mechanisms of disease.
What does a molecular biologist do on a daily basis?
On a daily basis, a molecular biologist may conduct laboratory experiments, analyze data, write and publish scientific papers, apply for grants, or collaborate with other scientists. They may also spend time reading the latest scientific literature to stay up-to-date in their field.
What is the difference between biochemistry and molecular biology?
While both fields study the biological processes at the molecular level, biochemistry focuses on the chemical reactions that make these processes happen, while molecular biology looks at the molecular interactions that control these reactions.
Sources
This post is part of my series on Molecular Biology.
Also check out my post: An Introduction to Molecular Biology: Unraveling the Basics and Immunofluorescence Staining: My Experience with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells
Sean Schepers is a third-year Medical Technology student at Mahidol University with a passion for all things health and medicine. His journey into the world of medicine has led him to explore various fields. Sean's blog posts offer a unique perspective, combining his academic insights with personal experiences. When he's not studying or blogging, Sean enjoys keeping up with politics and planning his future career in medicine.
In addition to his studies, Sean serves as the chairman of the Rights, Liberties, and Welfare Committee, a role that reflects his commitment to advocacy and social justice. Beyond his academic pursuits, Sean offers tutoring services in English and Biology, further demonstrating his dedication to education and mentorship. His journey is one of continuous discovery, and he invites others to join him as he explores the dynamic and transformative world of medical technology.