Monocytes and macrophages
Table of Contents
Key Summary Table: Monocytes and Macrophages
| Monocytes | Macrophages | |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Bloodstream | Tissues |
| Main Functions | Defense against foreign invaders, Inflammation, Transformation into macrophages | Engulfing and destroying pathogens, Antigen presentation, Cytokine release |
| Role in Diseases | Involved in various diseases, including atherosclerosis, cancer, and infectious diseases | Involved in various diseases, including atherosclerosis, cancer, and infectious diseases |
This article is a journey into the world of monocytes and macrophages, exploring their roles, their transformations, and their crucial roles in our immune response. It’s a journey that’s as fascinating as it is crucial, shedding light on the unsung heroes of our immune system and the incredible complexity of our health.
Introduction
The intricate workings of our immune system, and particularly the roles of monocytes and macrophages have always been fascinating. These cellular warriors work tirelessly to keep us healthy and free from disease. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of monocytes and macrophages, exploring their functions, their transformations, and their crucial roles in our immune response.
Monocytes and macrophages are fascinating. They tirelessly patrol our body, fighting off invaders and keeping us healthy
Monocytes and macrophages are part of the white blood cell family, the defenders of our body against foreign invaders. They are like the soldiers and the police of our body, always on the lookout for harmful intruders. Understanding their roles and functions can give us a deeper appreciation of the complexity and efficiency of our immune system.
This journey into the world of monocytes and macrophages is not just for those in the medical field. It’s for anyone who’s curious about how our bodies work, how we fight off diseases, and how we maintain our health. So, whether you’re a medical student, a health enthusiast, or just a curious reader, I invite you to join me on this fascinating exploration.
Understanding Hematology
Before we look at monocytes and macrophages, let’s take a moment to understand the broader field of Hematology. Hematology is the study of blood, blood-forming organs, and blood diseases. It’s a field that’s as vast as it is crucial, playing a key role in everything from diagnosing diseases to understanding our immune system.
Hematology is like a window into our health. By studying our blood, we can gain insights into our overall health, detect diseases early, and monitor our response to treatments. It’s a field that’s constantly evolving, with new discoveries and advancements being made every day.
In the context of Hematology, monocytes and macrophages play a crucial role. They are part of our white blood cells, the cells that make up our immune system. Understanding their functions and roles is key to understanding how our immune system works, how we fight off diseases, and how we maintain our health.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Hematology | The study of blood, blood-forming organs, and blood diseases |
| White Blood Cells | Cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders |
| Immune Response | The body’s defense system against foreign substances and pathogens |
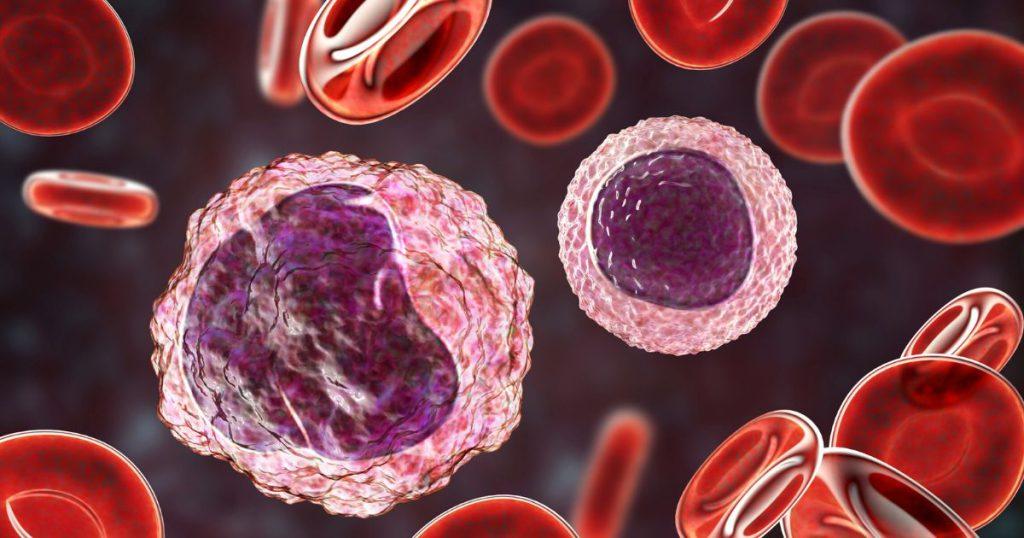
The Role of Monocytes in Our Immune System
Monocytes, the largest type of white blood cells, play a crucial role in our immune response. But what exactly are these roles? What are the 3 main functions of monocytes in immune response? Let’s delve deeper into these questions.
Firstly, monocytes act as our body’s first line of defense against foreign invaders. They patrol our bloodstream, on the lookout for harmful bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. When they detect these invaders, they quickly spring into action, engulfing and destroying them.
Secondly, monocytes play a crucial role in inflammation, our body’s response to injury or infection. They rush to the site of injury or infection, releasing substances that trigger inflammation. This helps to isolate the affected area and prevent the spread of infection.
Lastly, monocytes play a key role in the immune response by transforming into macrophages. This transformation allows them to perform more specialized functions, such as engulfing and destroying pathogens, presenting antigens to T cells, and releasing cytokines that regulate the immune response.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Defense | Act as the body’s first line of defense against foreign invaders |
| Inflammation | Play a crucial role in inflammation, the body’s response to injury or infection |
| Transformation | Can transform into macrophages when they enter the tissues |
The Transformation of Monocytes into Macrophages
One of the most fascinating aspects of monocytes is their ability to transform into macrophages. But what turns monocytes into macrophages? And are all macrophages developed from monocytes? Let’s explore these questions.
The transformation of monocytes into macrophages is triggered by signals from the tissues. When monocytes leave the bloodstream and enter the tissues, they are exposed to various signals that trigger their transformation into macrophages. This transformation allows them to perform more specialized functions, such as engulfing and destroying pathogens, presenting antigens to T cells, and releasing cytokines that regulate the immune response.
Not all macrophages are developed from monocytes. Some macrophages, known as resident macrophages, are already present in the tissues. These macrophages are long-lived and can self-renew, meaning they can maintain their population without the need for monocytes.
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Transformation | Triggered by signals from the tissues when monocytes leave the bloodstream and enter the tissues |
| Specialization | Allows monocytes to perform more specialized functions as macrophages |
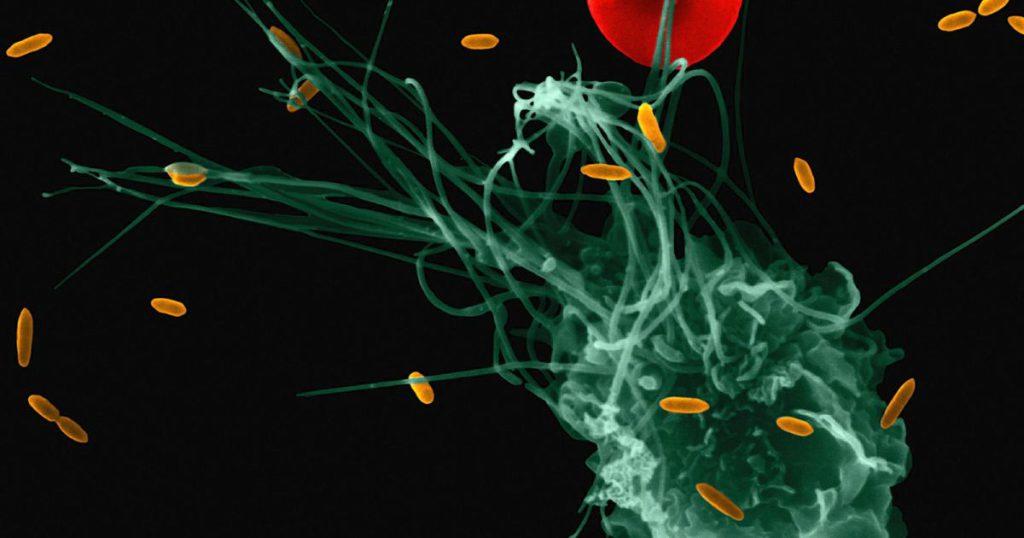
Macrophages: The Big Eaters of the Immune System
Macrophages, aptly named ‘big eaters’, are the body’s first line of defense against harmful pathogens. But what are the 3 main functions of macrophages in immune response? Let’s delve deeper into these questions.
Firstly, macrophages are responsible for phagocytosis, the process of engulfing and destroying pathogens. They are like the garbage collectors of our body, cleaning up dead cells, bacteria, and other debris.
Secondly, macrophages play a crucial role in antigen presentation. They process and present antigens to T cells, triggering the adaptive immune response. This allows our body to mount a more specific and effective defense against pathogens.
Lastly, macrophages release cytokines, small proteins that regulate the immune response. These cytokines can stimulate the immune response, attract other immune cells to the site of infection, and regulate inflammation.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Phagocytosis | Responsible for engulfing and destroying pathogens |
| Antigen Presentation | Process and present antigens to T cells, triggering the adaptive immune response |
| Cytokine Release | Release cytokines, small proteins that regulate the immune response |
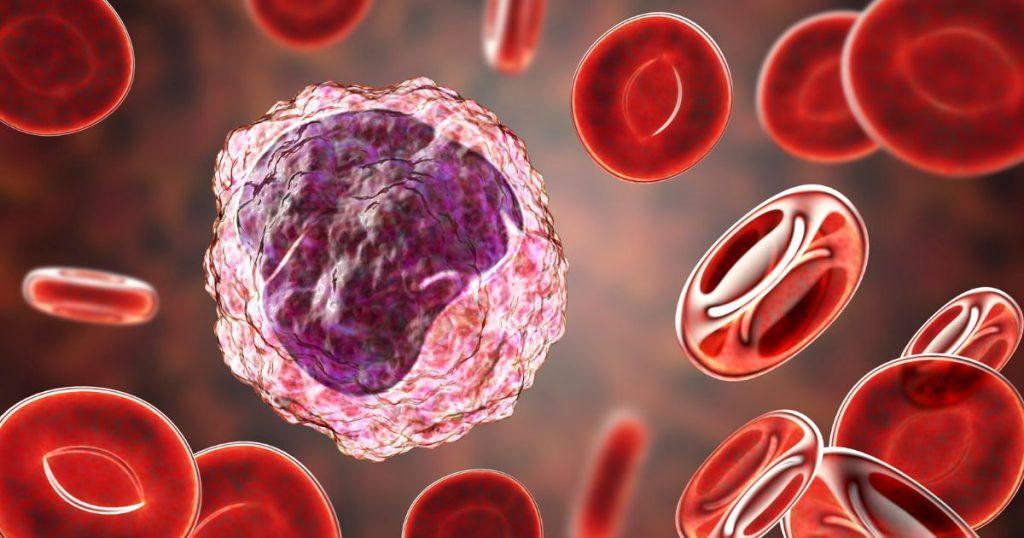
The Interplay between Monocytes and Macrophages in Disease
The interplay between monocytes and macrophages is not just crucial for our immune response, but also plays a significant role in various diseases. But what is the difference between a monocyte and a macrophage? And how are monocyte and macrophage similar? Let’s explore these questions.
Monocytes and macrophages are both types of white blood cells and part of our immune system. The main difference between them lies in their functions and locations. Monocytes are found in the bloodstream and act as our body’s first line of defense. They can transform into macrophages when they enter the tissues. Macrophages, on the other hand, are found in the tissues and perform more specialized functions, such as engulfing and destroying pathogens, presenting antigens to T cells, and releasing cytokines.
Despite their differences, monocytes and macrophages are similar in many ways. They are both crucial for our immune response, play key roles in inflammation, and are involved in the pathogenesis of various diseases, such as atherosclerosis, cancer, and infectious diseases.
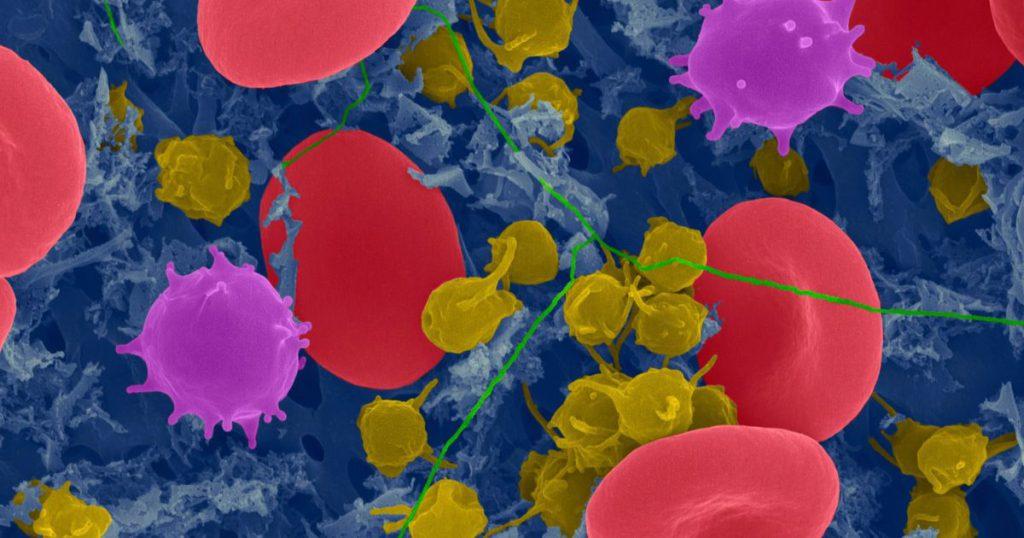
The immune system is not a single entity. We must think of it as a complex network of cells, including monocytes and macrophages, that work together to protect us from harmful pathogens.
Conclusion
The world of monocytes and macrophages is a testament to the incredible complexity and efficiency of our immune system. These cellular warriors are constantly working to keep us healthy, fighting off pathogens, triggering inflammation, and regulating our immune response. Understanding their roles and functions can give us a deeper appreciation of our health and the amazing workings of our body.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
If you find the captivating world of hematology as intriguing as I do, continue exploring this fascinating field. Visit my Hematology index page or the Hematology category for more in-depth articles and insights.
Other posts of interest: Lymphocytes and immune responses and Neutrophils and their role in infection
Frequently Asked Questions
What are monocytes and macrophages?
Monocytes and macrophages are types of white blood cells that play crucial roles in our immune system. Monocytes are found in the bloodstream and act as our body’s first line of defense against foreign invaders. Macrophages, on the other hand, are found in the tissues and perform more specialized functions, such as engulfing and destroying pathogens, presenting antigens to T cells, and releasing cytokines that regulate the immune response.
What is the main difference between monocytes and macrophages?
The main difference between monocytes and macrophages lies in their functions and locations. Monocytes are found in the bloodstream and can transform into macrophages when they enter the tissues. Macrophages, on the other hand, are found in the tissues and perform more specialized functions.
How do monocytes transform into macrophages?
The transformation of monocytes into macrophages is triggered by signals from the tissues. When monocytes leave the bloodstream and enter the tissues, they are exposed to various signals that trigger their transformation into macrophages.
What are the main functions of monocytes and macrophages in the immune response?
Monocytes and macrophages play crucial roles in our immune response. Monocytes act as our body’s first line of defense against foreign invaders, play a role in inflammation, and can transform into macrophages. Macrophages are responsible for engulfing and destroying pathogens, presenting antigens to T-cells, and releasing cytokines that regulate the immune response.
Are monocytes and macrophages involved in diseases?
Yes, the interplay between monocytes and macrophages is not just crucial for our immune response, but also plays a significant role in various diseases, such as atherosclerosis, cancer, and infectious diseases. Understanding their roles in these diseases can provide valuable insights into their pathogenesis and potential treatments.
Further Reading
Role of monocytes and macrophages in regulating immune …
Sean Schepers is a third-year Medical Technology student at Mahidol University with a passion for all things health and medicine. His journey into the world of medicine has led him to explore various fields. Sean's blog posts offer a unique perspective, combining his academic insights with personal experiences. When he's not studying or blogging, Sean enjoys keeping up with politics and planning his future career in medicine.
In addition to his studies, Sean serves as the chairman of the Rights, Liberties, and Welfare Committee, a role that reflects his commitment to advocacy and social justice. Beyond his academic pursuits, Sean offers tutoring services in English and Biology, further demonstrating his dedication to education and mentorship. His journey is one of continuous discovery, and he invites others to join him as he explores the dynamic and transformative world of medical technology.