Immunofluorescence Staining: My Experience with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells
Table of Contents
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells, a unique type of cancer cells, are the focus of our exploration today. Join me, as we dive into my personal journey of working with these cells, using immunofluorescence staining, and uncovering the mysteries they hold.
Introduction
Diving into the world of molecular biology and histology, I recently had an intriguing experience with immunofluorescence staining of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. This journey was not just about learning a new technique, but also about understanding the intricacies of cancer cells and the role of biomedical research in advancing our knowledge of such complex diseases.
Looking back on the experience, I realized that I had not only learned a lot about immunofluorescence staining and nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, but also about the process of scientific research.
The Biochemistry & Molecular Biology Summer Internship Training Program
My journey began when I enlisted in the Biochemistry & Molecular Biology Summer Internship Training Program. This program, designed to provide hands-on experience in the field of molecular biology, was a stepping stone into the world of biomedical research. It was here that I first encountered the concept of immunofluorescence staining and its application in studying nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
Understanding Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Before I could start working with them, I first had to understand what nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells were and why they were significant. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma is a type of cancer that occurs in the nasopharynx, the upper part of the throat behind the nose. It’s a relatively rare type of cancer but is particularly prevalent in certain parts of the world, including Southeast Asia. Studying these cells could provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of this disease and potentially lead to more effective treatments.
Now, you might be wondering, why nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells? Well, these cells are like the ‘bad guys’ in a superhero movie. They’re tough, they’re tricky, and they don’t play by the rules. They have a unique ability to grow and spread in ways that normal cells can’t, which makes them a challenging adversary in the fight against cancer. But just like in any good superhero movie, understanding the ‘bad guy’ is the first step to defeating them.
And that’s where the science comes in. By studying nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, we can learn more about how they operate. We can discover their weaknesses, their strengths, and their strategies. We can find out what makes them tick and, more importantly, what makes them stop ticking. It’s like being a detective, but instead of solving a crime, we’re trying to solve the mystery of cancer. And trust me, it’s just as exciting!
Based on the information from the American Cancer Society, here is a table summarizing some key statistics about Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Prevalence | Less than one case for every 100,000 people each year in most parts of the world, including the United States. However, it’s much more common in certain parts of South Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa. In some parts of China, there are as many as 25 to 30 cases per 100,000 men and 15 to 20 cases per 100,000 women. |
| Age of Diagnosis | In areas where the risk of NPC is high (such as China), the peak age of people being diagnosed is typically between 45 and 59. In areas of low risk of NPC (such as the US), cases can often be seen in young adulthood (ages 15 to 24) followed by a decline in cases until another peak at older ages of 65 to 79. |
| Gender Prevalence | Men are 2 to 3 times more likely to develop NPC than women. |
| Trend | Overall, cases of NPC have been declining steadily over the past decades, including in high-risk areas. This drop might be due to environmental and lifestyle changes. |
Please note that these statistics can vary based on various factors and it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for the most accurate information.
Cultivating the Cells
With a better understanding of the cells I was working with, the next step was to cultivate them in the lab. This process, known as cell cultivation, involves growing cells under controlled conditions. It’s a crucial part of biomedical research, allowing scientists to study cells in detail and observe how they respond to various stimuli. In my case, I was cultivating nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, a process that required careful monitoring and precise control of the growth conditions.
Cultivating these cells was like being a gardener, but instead of soil and seeds, I had petri dishes and cell cultures. The lab was my garden, and the cells were my crops. I had to provide the right environment for them to grow – a balanced pH, optimal temperature, and a nutrient-rich medium. Too much or too little of anything could upset their growth, so precision was key.
The cultivation process was a waiting game. It took about a week for the cells to multiply to the numbers I needed. During this time, I had to regularly check on them, making sure they were growing as expected. It was a test of patience and precision, but seeing the cells multiply and thrive was a rewarding experience. It was like watching a tiny universe unfold right before my eyes, a universe that held the secrets to understanding nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Immunofluorescence Staining: The Protocol
Once the cells were ready, it was time to dive into the main event: immunofluorescence staining. This technique involves using conjugated antibodies to tag specific proteins within the cells, then using a fluorescent dye to make these proteins visible under a microscope. In the context of my project, I was using immunofluorescence staining to study the localization of certain proteins within the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
The process began with the preparation of the cells. They were fixed using formaldehyde, a chemical that helps preserve the structure of the cells and their components. This step is crucial as it prevents any changes in the cells during the staining process. It’s kind of like freezing a moment in time, allowing us to take a closer look at the cells in their natural state.
Immunofluorescence Staining Steps
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Cell Cultivation | Cultivating nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in the lab |
| Fixation | Using formaldehyde to fix the cells |
| Staining | Applying antibodies to stain different parts of the cell |
| Visualization | Using Olympus Fluoview to visualize the proteins |
Next came the actual staining. The antibodies, which are like tiny homing devices, were introduced to the cells. Each antibody is designed to find and attach to a specific protein. Once the antibodies had found their targets, it was time for the fluorescent dye. This dye binds to the antibodies, essentially putting a spotlight on the proteins we’re interested in. It’s a bit like playing a game of hide and seek, but in this case, the antibodies are doing the seeking, and the proteins are doing the hiding.
After the staining, the cells were washed to remove any unbound antibodies and dye. This step is like cleaning up after a party, making sure only the guests (antibodies) that found their partners (proteins) stay. This ensures that the final image isn’t cluttered with unwanted noise.
The final step was to mount the cells onto slides and examine them under the Olympus Fluoview microscope. This part always feels a bit like a grand reveal, the moment when all the hard work pays off. As the cells came into focus, the proteins we tagged lit up, creating a beautiful, glowing map of cellular activity. Each color represented a different protein, painting a vivid picture of the inner workings of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
Visualizing Proteins with Olympus Fluoview
After the staining was complete, it was time to visualize the proteins using a high-tech microscope called the Olympus Fluoview. This microscope uses laser light to excite the fluorescent dyes, causing them to emit light that can be detected and translated into an image. Using this microscope, I was able to see the localization of the proteins within the cells, providing valuable insights into their function and behavior.
The Olympus Fluoview is not your average high school microscope. It’s like the superhero of microscopes, capable of revealing the tiniest details with incredible clarity. Imagine being able to see the minute structures within a cell, almost like having x-ray vision. It’s a bit like peering into a secret world, a world that is bustling with activity and full of surprises.
The process of capturing the images was a delicate dance. It required careful calibration of the microscope, precise positioning of the sample, and a steady hand to capture the best possible image. But the effort was worth it. Each image was a snapshot of life at the molecular level, a glimpse into the intricate workings of the cell. It was like being a detective, piecing together clues to unravel the mysteries of cellular function.
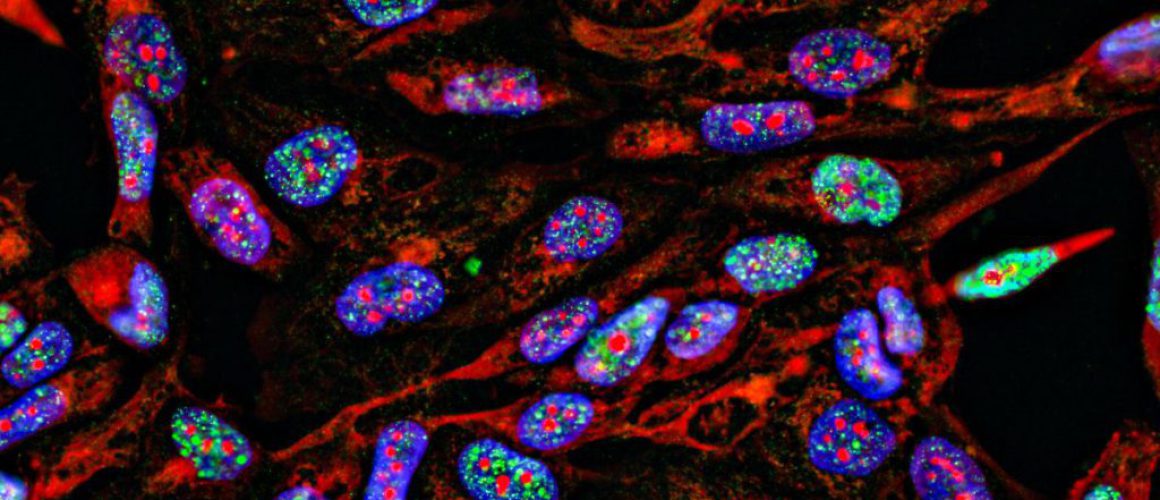
Interpreting the Images
With the images captured, the next challenge was interpreting what they meant. This involved understanding the function of the proteins I was studying, as well as how their localization might affect the behavior of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. It was a complex process, but one that was crucial for making sense of the data I had gathered.
Now, let’s talk about the colors. In the world of immunofluorescence, colors are more than just a visual aid – they’re the language we use to understand what’s happening inside the cell. In my case, the red and blue colors were not just for show. They were actually representing different components of the cell. The red color was a result of the specific antibody I used, which was designed to attach to a particular protein of interest. This protein was then visualized under the microscope as a red glow, giving me a clear picture of where this protein was located within the cell.
The blue, on the other hand, was staining the cell’s nucleus. The nucleus is like the control center of the cell, holding most of the cell’s genetic material. By staining it blue, I could clearly distinguish it from the rest of the cell. This was important because it allowed me to see if the red-stained protein was in the nucleus, outside of it, or both. Understanding this localization can provide valuable insights into how the protein functions and how it might be contributing to the behavior of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
Key Findings and Insights
The process was challenging, but it led to some fascinating findings and insights. For instance, I observed that certain proteins were localized in specific parts of the cells, suggesting that they might play a role in the cells’ ability to proliferate and invade surrounding tissues. These findings could potentially lead to new targets for cancer treatments, highlighting the importance of this type of research.
As I delved deeper into the data, I noticed patterns emerging. The red stain, which marked a particular protein, seemed to cluster around the blue-stained nucleus. This was like finding a secret hideout in a game of hide-and-seek, revealing where this protein liked to hang out. It was a eureka moment, as this could mean that this protein has a significant role in the cell’s nucleus, possibly in controlling cell functions or even the cell’s behavior.
Moreover, the intensity of the staining also provided valuable insights. Some cells showed a stronger red stain than others, which could indicate varying levels of protein expression. This variation could be a reflection of the heterogeneous nature of cancer cells, where not all cells are identical. Understanding this heterogeneity is crucial as it can influence the response to treatment and the overall progression of the disease.
Key Findings from the Experiment
| Finding | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Protein Localization | The red color showed the localization of certain proteins |
| Cell Structure | The staining revealed the structure of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells |
| Research Process | The experiment provided insights into the process of scientific research |
Reflections on the Experience
Looking back on the experience, I realized that I had not only learned a lot about immunofluorescence staining and nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, but also about the process of scientific research. I learned that research is not just about following a set protocol, but also about asking questions, interpreting data, and making connections between different pieces of information. It was a challenging but rewarding experience that deepened my understanding of molecular biology and histology.
In the midst of all the lab work, I also discovered the importance of patience and precision. Each step in the staining process had to be executed with meticulous care. A slight deviation could potentially alter the results, leading to inaccurate conclusions. This experience taught me the value of attention to detail in scientific research. It’s not just about getting to the end result, but about understanding each step that leads you there.
Moreover, I was struck by the beauty and complexity of the microscopic world. Observing the stained cells under the Olympus Fluoview microscope, I was in awe of the intricate structures and patterns that were revealed. It was a vivid reminder of the incredible complexity of life at the cellular level. This experience has not only enriched my knowledge and skills in molecular biology, but also deepened my appreciation for the beauty and wonder of life’s smallest building blocks.
Key Learnings from the Experience
- Understanding the process of immunofluorescence staining
- Gaining hands-on experience with lab equipment like Olympus Fluoview
- Learning about the structure and behavior of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- Gaining insights into the process of scientific research
Immunofluorescence staining of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells was a complex process, but it was also an incredibly rewarding experience that deepened my understanding of molecular biology and histology.
Conclusion
Immunofluorescence staining of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells was a complex process, but it was also an incredibly rewarding experience that deepened my understanding of molecular biology and histology. It was a journey of discovery, filled with challenges and surprises, but also with moments of insight and understanding. It was a reminder of the power of scientific research and the potential it holds for improving our understanding of diseases like cancer.
In the end, this experience was not just about learning a new technique or studying a specific type of cancer cell. It was about understanding the process of scientific research and the role it plays in advancing our knowledge of the world. It was a reminder of the importance of curiosity, perseverance, and a willingness to delve into the unknown. And it was a testament to the power of science to shed light on the mysteries of the natural world.
This post is part of the Molecular Biology category and belongs to the series Molecular Biology: A Comprehensive Guide for Medical Technology
Also have a look at my other posts: The Role of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Techniques in Understanding Genetic Disorders and Deciphering the Genetic Code: The Role of DNA and RNA in Molecular Biology
Remember, the world of science is vast and full of mysteries waiting to be discovered. So don’t be afraid to dive in, ask questions, and explore. You never know what you might find.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Immunofluorescence Staining?
Immunofluorescence Staining is a technique used in biomedical research to detect specific proteins within cells using antibodies that are tagged with fluorescent dyes. This method allows researchers to visualize and study the localization of these proteins under a microscope.
What are the types of Immunofluorescence Staining?
There are two main types of Immunofluorescence Staining: direct and indirect. Direct staining involves using a fluorescently labeled primary antibody that binds directly to the target protein. Indirect staining, on the other hand, involves an unlabeled primary antibody that binds to the target protein and a fluorescently labeled secondary antibody that binds to the primary antibody.
What is the role of formaldehyde in Immunofluorescence Staining?
Formaldehyde is used to fix the cells during the staining process. This chemical helps preserve the structure of the cells and their components, preventing any changes in the cells during the staining process. It’s like freezing a moment in time, allowing researchers to take a closer look at the cells in their natural state.
What is the significance of Immunofluorescence Staining in cancer research?
Immunofluorescence Staining plays a crucial role in cancer research. It allows researchers to study the localization of specific proteins within cancer cells, such as nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. This can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of cancer development and progression, and can also aid in the development of targeted cancer therapies.
What is Olympus Fluoview and how is it used in Immunofluorescence Staining?
Olympus Fluoview is a high-tech microscope used to visualize the proteins after the staining process in Immunofluorescence Staining. After the antibodies have found their targets and the fluorescent dye has been applied, the Olympus Fluoview microscope is used to capture images of the glowing cells, each one telling its own unique story.
What is the process of interpreting the images obtained from Immunofluorescence Staining?
Interpreting the images obtained from Immunofluorescence Staining involves analyzing the localization and distribution of the fluorescently labeled proteins within the cells. This can provide insights into the function of these proteins and their role in the cell’s behavior. For example, in the context of cancer cells, this can help researchers understand how these proteins contribute to cancer development and progression.
What are the key findings and insights that can be obtained from Immunofluorescence Staining?
The key findings and insights from Immunofluorescence Staining can vary depending on the specific proteins being studied and the type of cells being used. In the context of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, for example, this technique can provide insights into the localization of specific proteins within the cells, which can in turn provide valuable information about the mechanisms of cancer development and progression.
What are the challenges and rewards of Immunofluorescence Staining?
While Immunofluorescence Staining is a complex process that requires careful preparation and execution, it is also an incredibly rewarding technique that can provide deep insights into cell biology. It allows researchers to visualize specific proteins within cells, providing a unique window into the inner workings of these cells. This can lead to important discoveries and advancements in biomedical research.
Further reading
National Institutes of Health: An introduction to Performing Immunofluorescence Staining
Sean Schepers is a third-year Medical Technology student at Mahidol University with a passion for all things health and medicine. His journey into the world of medicine has led him to explore various fields. Sean's blog posts offer a unique perspective, combining his academic insights with personal experiences. When he's not studying or blogging, Sean enjoys keeping up with politics and planning his future career in medicine.
In addition to his studies, Sean serves as the chairman of the Rights, Liberties, and Welfare Committee, a role that reflects his commitment to advocacy and social justice. Beyond his academic pursuits, Sean offers tutoring services in English and Biology, further demonstrating his dedication to education and mentorship. His journey is one of continuous discovery, and he invites others to join him as he explores the dynamic and transformative world of medical technology.