Acid-fast staining (Ziehl-Neelsen, Kinyoun) and interpretation
Table of Contents
Key Summary Table: Acid-fast Staining
| Staining Method | Heat Required | Staining Time | Stain Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ziehl-Neelsen | Yes | Short | Less Concentrated |
| Kinyoun | No | Long | More Concentrated |
Welcome to the vibrant world of “Acid-fast staining”! This nifty technique, a superstar in the realm of medical technology, helps us spot certain bacteria that other methods can’t. Stick around as we unravel the mysteries of Ziehl-Neelsen and Kinyoun staining techniques, and why they’re so crucial in healthcare.
Understanding Acid-fast Staining
Acid-fast staining, a term that might sound complex, but it’s a fascinating world once you get to know it. It’s a unique staining technique that has been a cornerstone in the field of medical technology. This technique is particularly important for identifying certain types of bacteria that are not easily stained by other methods, making it a crucial tool in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases.
In the realm of medical technology, acid-fast staining stands as a testament to the power of simple techniques to reveal complex truths.
The term “acid-fast” refers to the property of these bacteria to retain the primary stain even after being treated with an acid-alcohol solution during the staining process. This characteristic is due to the high lipid content in their cell walls, which makes them resistant to decolorization. Understanding this technique is not just about knowing the steps involved, but also about appreciating its significance in the broader context of healthcare and disease control.
Advantages of Acid-fast Staining
- Ability to identify certain types of bacteria that are not easily stained by other methods
- Useful in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases
- Simple and cost-effective technique
- Provides valuable information about the cell wall properties of bacteria
The Three Types of Acid-fast Staining
| Staining Type | Dye Used | Microscope Required |
|---|---|---|
| Ziehl-Neelsen | Carbol Fuchsin | Regular Microscope |
| Kinyoun | Carbol Fuchsin | Regular Microscope |
| Auramine-rhodamine | Fluorescent Dyes | Fluorescence Microscope |
When it comes to acid-fast staining, there are three main types that you should be aware of: Ziehl-Neelsen, Kinyoun, and Auramine-rhodamine. Each of these has its own unique characteristics and applications, but they all serve the same fundamental purpose – to identify acid-fast bacteria.
The Ziehl-Neelsen and Kinyoun methods are the most traditional and widely used techniques. They both involve the use of a strong dye, typically carbol fuchsin, which penetrates the waxy cell wall of the bacteria and imparts a bright red color. The Auramine-rhodamine method, on the other hand, uses fluorescent dyes that bind to the mycolic acids in the cell wall, making the bacteria glow under a fluorescence microscope.
Hot Method vs Cold Method in Acid-fast Staining
| Method | Heat Required | Staining Time |
|---|---|---|
| Hot | Yes | Shorter |
| Cold | No | Longer |
Now, let’s talk about the hot and cold methods of acid-fast staining. These terms might sound like they’re about temperature, but they’re actually about the way the primary stain is applied. In the hot method, which is used in the Ziehl-Neelsen technique, the stain is heated to help it penetrate the waxy cell wall of the bacteria. This is usually done by gently heating the slide over a flame while the stain is applied.
The cold method, used in the Kinyoun technique, doesn’t involve any heating. Instead, it uses a more concentrated stain and a longer staining time to achieve the same result. Both methods have their pros and cons, and the choice between them often depends on the resources available and the specific requirements of the laboratory.
Ziehl-Neelsen vs Kinyoun: A Comparative Study
| Method | Heat Required | Stain Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| Ziehl-Neelsen | Yes | Less Concentrated |
| Kinyoun | No | More Concentrated |
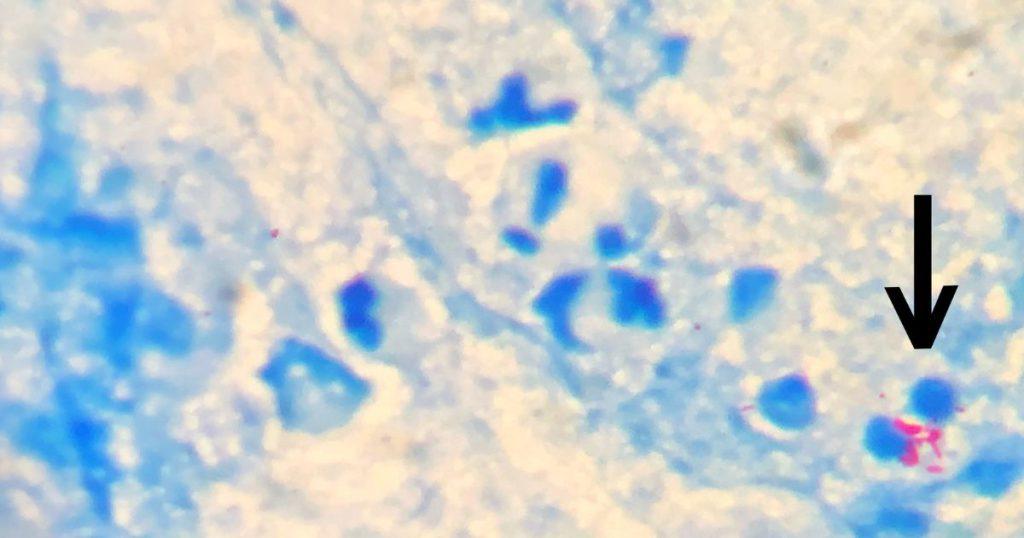
So, what’s the difference between the Ziehl-Neelsen and Kinyoun methods? Well, as we’ve already discussed, the main difference lies in the application of the primary stain. But there’s more to it than just that. The Ziehl-Neelsen method, also known as the hot method, requires the use of heat to facilitate the penetration of the stain. This can be a bit tricky, as it requires careful control of the heat to prevent overheating and damaging the sample.
The Kinyoun method, on the other hand, is a cold staining method that doesn’t require heat. This makes it a bit simpler and safer to perform, but it also requires a more concentrated stain and a longer staining time. Both methods are effective for identifying acid-fast bacteria, and the choice between them often comes down to practical considerations.
Interpreting the Results of Acid-fast Staining
| Result | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Red Bacteria, Blue Background | Positive for Acid-fast Bacteria |
| Blue Bacteria, Blue Background | Negative for Acid-fast Bacteria |
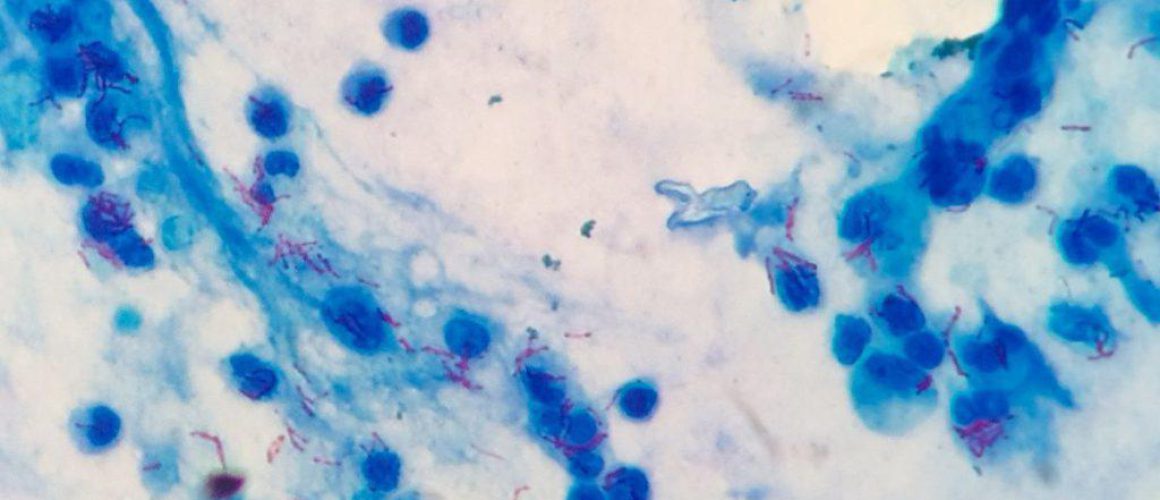
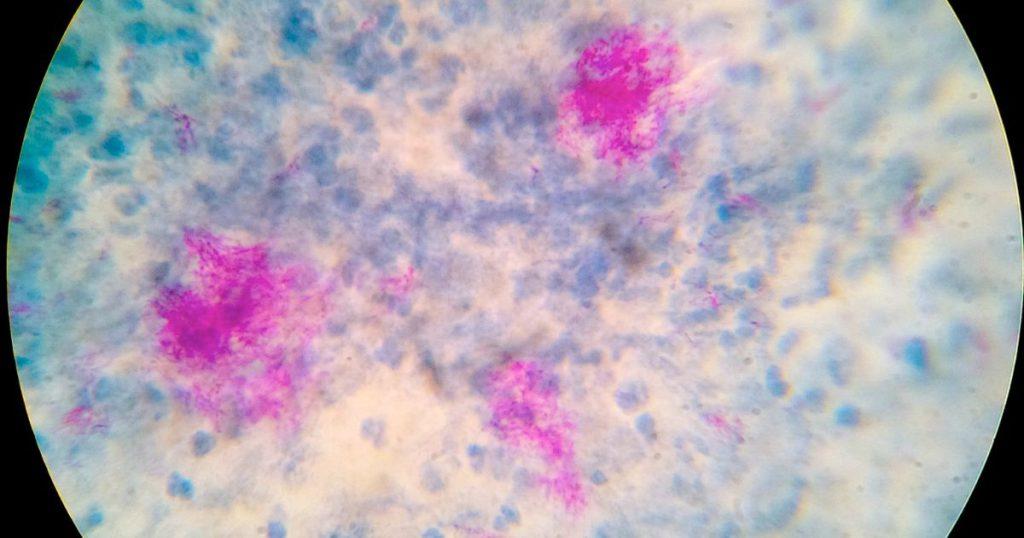
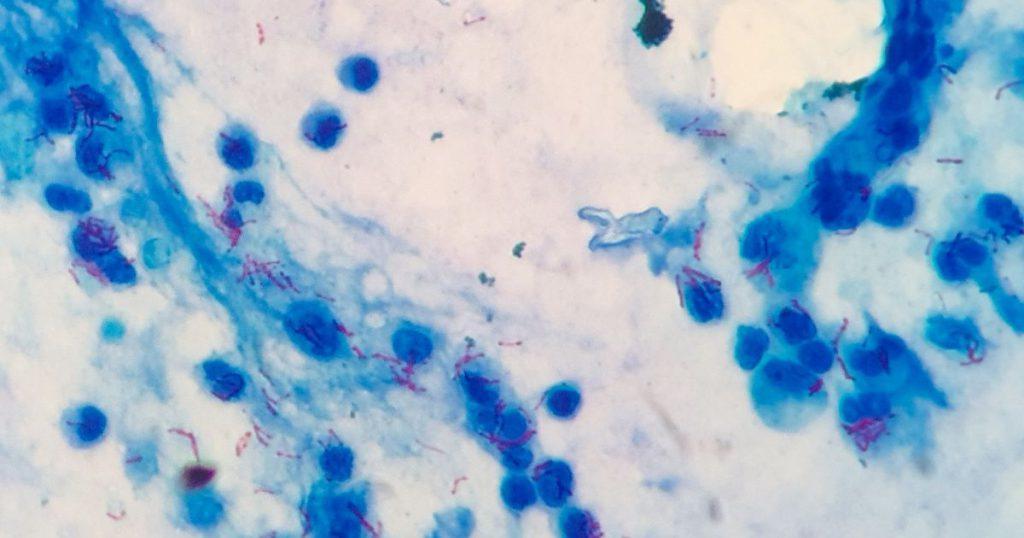
Interpreting the results of acid-fast staining is a skill that requires knowledge, experience, and a keen eye for detail. Under the microscope, acid-fast bacteria will appear bright red against a blue background. This is because they retain the red primary stain, while the non-acid-fast cells take up the blue counterstain.
Interpretation is not always straightforward. Sometimes, the staining may be uneven, or there may be other elements in the sample that can confuse the interpretation. Therefore, it’s important to always consider the staining results in the context of other clinical and laboratory findings.
The Unique Components of Ziehl-Neelsen Staining Technique
The Ziehl-Neelsen staining technique has some unique components that set it apart from other staining methods. One of these is the use of phenol in the primary stain, which helps to solubilize the dye and facilitate its penetration into the bacteria. Another unique component is the use of a strong decolorizer, typically an acid-alcohol solution, which removes the stain from non-acid-fast cells but is resisted by the acid-fast bacteria.
Unique Components of Ziehl-Neelsen Staining Technique
- Use of phenol in the primary stain
- Use of a strong decolorizer
- Retention of the red primary stain by acid-fast bacteria
- Use of heat to facilitate the penetration of the stain
Acid-fast staining is a window into a world that’s invisible to the naked eye, a world that holds the keys to understanding and combating some of the most challenging diseases of our time.
Conclusion
In the realm of medical technology, acid-fast staining stands as a testament to the power of simple techniques to reveal complex truths. It’s a window into a world that’s invisible to the naked eye, a world that holds the keys to understanding and combating some of the most challenging diseases of our time.
This post is part of my Clinical Microscopy category. Please check out index page on Clinical Microscopy
Other pages of interest: Staining in Clinical Microscopy: Revealing the Invisible and Fungal staining (KOH, Calcofluor White) and interpretation
This post is part of my Bacteriology category. Also check out my index page on Bacteriology.
Other pages of interest: Bacterial classification and taxonomy and Gram staining and interpretation
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be used as a replacement for professional medical advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the three types of acid-fast staining?
The three main types of acid-fast staining are Ziehl-Neelsen, Kinyoun, and Auramine-rhodamine. Each of these methods has its own unique characteristics and applications, but they all serve the same fundamental purpose – to identify acid-fast bacteria.
What is the difference between the hot method and the cold method of acid-fast staining?
The hot method, used in the Ziehl-Neelsen technique, involves heating the stain to help it penetrate the waxy cell wall of the bacteria. The cold method, used in the Kinyoun technique, doesn’t involve any heating but uses a more concentrated stain and a longer staining time to achieve the same result.
What is the difference between the Zn acid fast stain and the Kinyoun acid fast stain?
The main difference between the Zn (Ziehl-Neelsen) and Kinyoun acid-fast stains lies in the application of the primary stain. The Zn method uses heat to facilitate the penetration of the stain, hence it’s often referred to as the hot method. On the other hand, the Kinyoun method doesn’t require heat and uses a more concentrated stain with a longer staining time, hence it’s known as the cold method.
What is the result interpretation of acid-fast staining?
Under the microscope, acid-fast bacteria will appear bright red against a blue background. This is because they retain the red primary stain, while the non-acid-fast cells take up the blue counterstain. However, interpretation is not always straightforward and should always be considered in the context of other clinical and laboratory findings.
What is the difference between Zn and Kinyoun methods?
The main difference between the Zn (Ziehl-Neelsen) and Kinyoun methods is the application of the primary stain. The Zn method uses heat to facilitate the penetration of the stain, while the Kinyoun method doesn’t require heat and uses a more concentrated stain with a longer staining time.
What is used in the Ziehl-Neelsen staining technique that is not used in the Kinyoun staining techniques?
The Ziehl-Neelsen staining technique uses heat to facilitate the penetration of the primary stain into the bacteria. This is not required in the Kinyoun staining technique, which instead uses a more concentrated stain and a longer staining time.
Further reading
Kinyoun Stain – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Sean Schepers is a third-year Medical Technology student at Mahidol University with a passion for all things health and medicine. His journey into the world of medicine has led him to explore various fields. Sean's blog posts offer a unique perspective, combining his academic insights with personal experiences. When he's not studying or blogging, Sean enjoys keeping up with politics and planning his future career in medicine.
In addition to his studies, Sean serves as the chairman of the Rights, Liberties, and Welfare Committee, a role that reflects his commitment to advocacy and social justice. Beyond his academic pursuits, Sean offers tutoring services in English and Biology, further demonstrating his dedication to education and mentorship. His journey is one of continuous discovery, and he invites others to join him as he explores the dynamic and transformative world of medical technology.